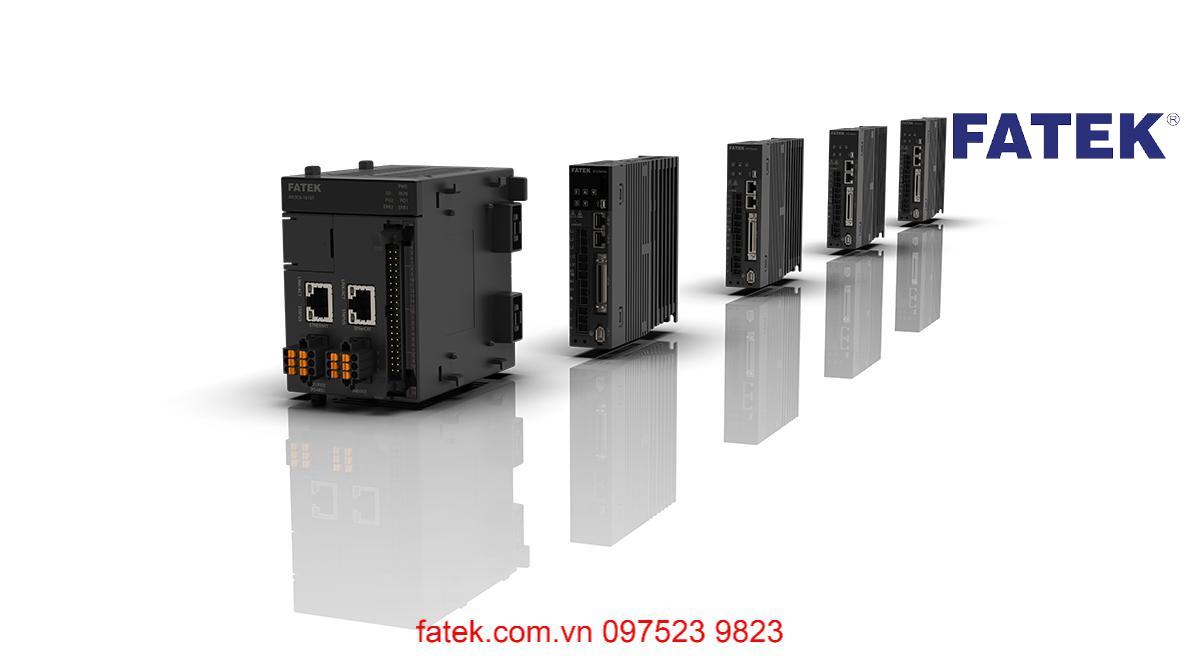
Classify Fatek Servos by size

- Small Servos: These are compact servo motors suitable for applications where space is limited or where smaller loads need to be controlled with precision.
- Medium Servos: These servos are larger and more powerful, capable of handling moderate to heavy loads while still maintaining accuracy and responsiveness.
- Large Servos: These are heavy-duty servo motors designed for industrial applications requiring high torque and precision control, such as robotic arms or CNC machinery.
- Extra-Large Servos: In some cases, particularly in heavy industrial settings or specialized applications, there might be a need for extra-large servo motors capable of handling extremely heavy loads.
Classify Fatek Servos according to motor type
Fatek servos can be classified according to two main motor types: brushless DC motors and permanent magnet AC synchronous motors [source].
Brushless DC (BLDC) Motors
These are the most common type of servo motor used in industrial automation. They use a DC power source but have their brushes replaced with electronically controlled switches. This design offers several advantages over brushed DC motors, including:
- Higher efficiency and longer lifespan due to reduced friction
- Lower maintenance requirements since there are no brushes to wear out
- Improved speed control due to precise electronic commutation
BLDC motors are generally smaller and lighter than AC synchronous motors, making them well-suited for applications requiring high speed and precision control.
Permanent Magnet AC Synchronous Motors
These motors use a permanent magnet rotor and a stator with windings that are energized by an AC current. The interaction between the magnetic fields creates torque that rotates the motor shaft. AC synchronous motors offer several advantages over BLDC motors, including:
- Higher torque output, making them suitable for demanding applications
- Simpler motor construction, potentially leading to lower cost
- Higher operating speeds
Fatek servos can be classified according to two main controller types: analog controllers and intelligent controllers [source].
Analog Controllers
Analog controllers are the simpler type of servo controller. They receive an analog voltage signal as input, which corresponds to the desired position, speed, or torque of the servo motor. The controller then amplifies this signal to drive the servo motor.
Analog controllers are typically less expensive and easier to set up than intelligent controllers. However, they offer less flexibility and control over the servo motor. For instance, they cannot perform complex motion profiles or compensate for errors.
- Implementing complex motion profiles
- Compensating for errors
- Communicating with other devices on a network
Intelligent Controllers
Intelligent controllers are more sophisticated than analog controllers. They use a microprocessor to control the servo motor and can receive digital signals as input. This allows for more precise control of the servo motor’s position, speed, and torque.
Intelligent controllers can also perform a wider range of functions, such as:
- Implementing complex motion profiles
- Compensating for errors
- Communicating with other devices on a network
Some typical Fatek Servo types

Here are some typical Fatek Servo types classified according to their motor type:
By Motor Type
-
BLDC Servos (FSD-A, FSD-H):
- Motor Type: Brushless DC Motor
- Size: Compact (FSD-A) and Large (FSD-H)
- Torque: Low to Medium (FSD-A), High (FSD-H)
- Applications: Simple automation (FSD-A), Industrial machinery, Mini robots (FSD-H)
- Pros: High efficiency, long lifespan, precise speed control (especially FSD-A)
- Cons: Lower torque output compared to PMSM (especially FSD-A)
-
Permanent Magnet AC Synchronous Servos (FSV-A, FSV-H):
- Motor Type: Permanent Magnet AC Synchronous Motor
- Size: Compact (FSV-A) and Large (FSV-H)
- Torque: Medium (FSV-A), High (FSV-H)
- Applications: Arm robots, 3D printers (FSV-A), Industrial robots, Autonomous vehicles (FSV-H)
- Pros: Higher torque output compared to BLDC (especially FSV-H), simpler motor construction
- Cons: Generally larger and heavier than BLDC, less precise speed control (especially FSV-H)
By Controller Type (Note: Model designations are not confirmed)
-
Analog Servo Drives: Likely available for different power ratings and motor sizes (FSD-A, FSV-A).
- Control Type: Analog controller
- Pros: Simpler and more affordable option
- Cons: Less flexible and limited control over the servo motor
-
Intelligent Servo Drives: Likely available for various power and motor size options (FSD-H, FSV-H).
- Control Type: Intelligent controller with microprocessor
- Pros: Precise control, complex motion profiles, communication with other devices
- Cons: More expensive and complex to set up
Application of Servo Fatek
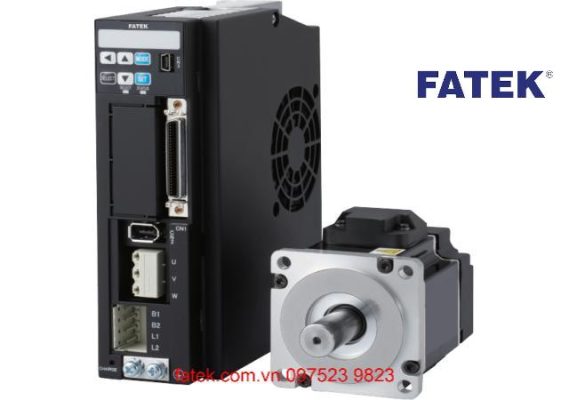

- Industry: Servo motors are used in industrial automation systems such as robots, CNC machines, packaging machines, etc.
- Medical: Servo motors are used in medical equipment such as X-ray machines, ultrasound machines, surgical robots, etc.
- Building automation: Servo motors are used in automatic control systems for elevators, doors, ventilation systems, etc.
- Robot: Servo motor is an important part in robots, helping the robot move and perform precise operations.
- Drones: Servo motors are used in drones to control altitude, flight direction and stability.
Choose the suitable Fatek Servo
- Feedback System: Decide on the type of feedback system needed for precise position control. Options may include incremental encoders, absolute encoders, or resolver feedback. Select a servo with a feedback system that meets your accuracy and resolution requirements.
- Size and Mounting: Ensure that the physical dimensions and mounting configuration of the servo motor are compatible with your application’s space constraints and mounting requirements.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, vibration, and dust exposure in your application environment. Choose a servo motor with appropriate protection ratings (e.g., IP65) to ensure reliable operation under these conditions.
- Communication and Control Interface: Check compatibility with your control system and communication protocols (e.g., EtherCAT, Modbus, CANopen). Ensure that the servo motor can be seamlessly integrated into your existing automation setup
Communications
FATEK VIETNAM COMPANY
Website: https://fatek.com.vn/
Hotline: 097 523 9823


 English
English Français
Français 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어
